1,4-Dimethoxybenzene: A Detailed Overview
1,4-Dimethoxybenzene, often referred to as p-dimethoxybenzene, is a compound that has garnered significant interest in various fields, including organic chemistry, pharmaceuticals, and materials science. This compound is characterized by its unique structure and properties, which make it a valuable molecule in both research and industrial applications. In this article, we will delve into the details of 1,4-dimethoxybenzene, exploring its synthesis, properties, uses, and safety considerations.
Synthesis of 1,4-Dimethoxybenzene
The synthesis of 1,4-dimethoxybenzene typically involves the reaction of a phenol derivative with formaldehyde and sodium hydroxide. One common method is the reaction of 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde with formaldehyde and sodium hydroxide in an aqueous solution. The reaction proceeds via a condensation reaction, resulting in the formation of 1,4-dimethoxybenzene. The overall reaction can be represented as follows:
| Reactants | Products |
|---|---|
| 4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde + Formaldehyde + Sodium Hydroxide | 1,4-Dimethoxybenzene + Water |
After the reaction is complete, the product is typically purified through recrystallization from a suitable solvent, such as ethanol or methanol.
Properties of 1,4-Dimethoxybenzene
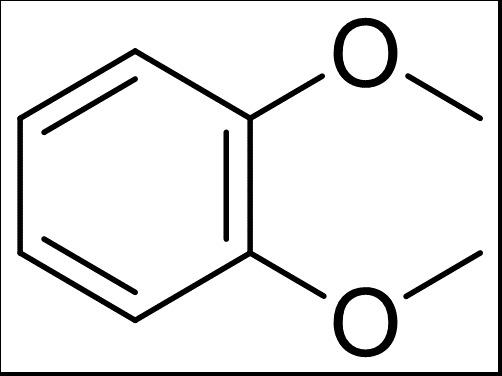
1,4-Dimethoxybenzene is a white solid with a melting point of approximately 70-72掳C. It has a characteristic odor and is soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, and chloroform. The compound is also slightly soluble in water. Its molecular formula is C8H10O2, and it has a molecular weight of 150.18 g/mol. The compound’s structure consists of a benzene ring with two methoxy groups attached to the 1 and 4 positions.
1,4-Dimethoxybenzene is a weak base, with a pKa value of around 10.5. This property makes it useful in certain chemical reactions, such as the formation of esters and amides. Additionally, the compound is a ligand in coordination chemistry, forming stable complexes with transition metals.
Uses of 1,4-Dimethoxybenzene
1,4-Dimethoxybenzene has a variety of applications in different industries. Some of the most notable uses include:
-
Pharmaceuticals: The compound is used as a starting material for the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals, including analgesics, anti-inflammatory agents, and antiviral drugs.
-
Materials Science: 1,4-Dimethoxybenzene is used in the synthesis of polyesters, polyimides, and other polymers. These polymers find applications in various industries, such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
-
Agrochemicals: The compound is used in the synthesis of herbicides and insecticides, contributing to the development of more effective agricultural products.
-
Flavors and Fragrances: 1,4-Dimethoxybenzene is used in the production of flavors and fragrances, adding unique scents and tastes to various products.
Safety Considerations
While 1,4-dimethoxybenzene has numerous applications, it is important to consider its safety profile. The compound is classified as a hazardous substance, and exposure to it can cause various health issues. Some of the potential risks associated with 1,4-dimethoxybenzene include:
-
Inhalation: Exposure to the vapor can cause respiratory irritation, coughing, and shortness of breath.
-
Ingestion: Consumption of the compound can lead to nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
-
Dermal Contact: Contact with the skin can cause irritation, redness, and allergic reactions.
As a result, it is crucial to handle 1,4-dimethoxybenzene with appropriate safety