1 in Polar Areas: Solar Radiation Strikes Earth at Angle a
Understanding the angle at which solar radiation strikes the Earth, particularly in polar regions, is crucial for comprehending various environmental and climatic phenomena. This article delves into the intricacies of solar radiation in polar areas, focusing on the angle ‘a’ at which it impacts the Earth’s surface.
What is Solar Radiation?
Solar radiation refers to the energy emitted by the Sun in the form of electromagnetic waves. This energy is the primary source of heat and light on Earth. The intensity of solar radiation varies depending on several factors, including the angle at which it strikes the Earth’s surface.
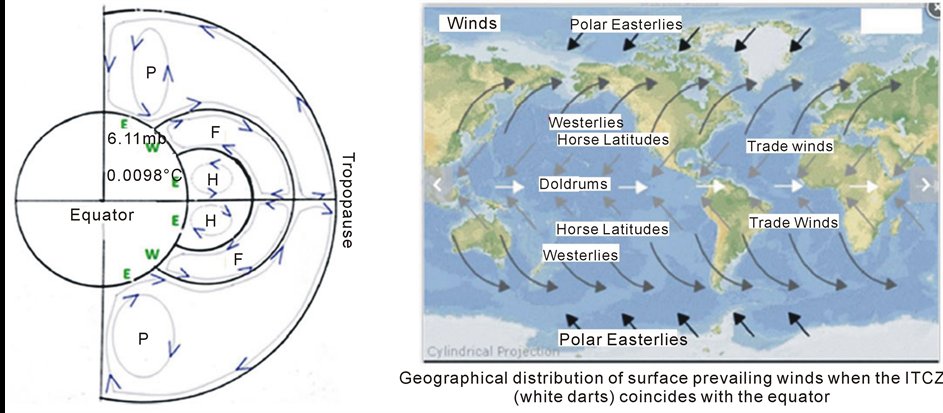
The Angle of Incidence
The angle of incidence, denoted as ‘a’, is the angle between the incoming solar radiation and the Earth’s surface. In polar regions, this angle can vary significantly throughout the year, affecting the amount of solar radiation received.
Impact of Angle ‘a’ in Polar Areas
In polar regions, the angle ‘a’ plays a crucial role in determining the intensity of solar radiation. Here are some key impacts of this angle:
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Seasonal Variations | The angle ‘a’ varies throughout the year, leading to seasonal changes in solar radiation intensity. During summer months, the angle is relatively low, resulting in higher solar radiation levels. Conversely, during winter months, the angle is higher, leading to lower solar radiation levels. |
| Glacier Melting | In polar regions, the angle ‘a’ affects the melting of glaciers. Higher solar radiation intensity during summer months accelerates the melting process, contributing to rising sea levels. |
| Vegetation Growth | The angle ‘a’ influences the growth of vegetation in polar regions. During the short growing season, the angle determines the amount of solar radiation available for photosynthesis, affecting plant growth and productivity. |
| Climate Change | The angle ‘a’ is a critical factor in understanding climate change in polar regions. Changes in the angle can lead to shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns, impacting the overall climate system. |
Understanding the angle ‘a’ and its impact on polar regions is essential for policymakers, scientists, and researchers. By analyzing the angle’s influence on various environmental and climatic phenomena, we can better predict and mitigate the effects of climate change in these sensitive areas.
Measurement of Angle ‘a’
Measuring the angle ‘a’ is crucial for studying solar radiation in polar regions. Various instruments and techniques are used to determine this angle, including:
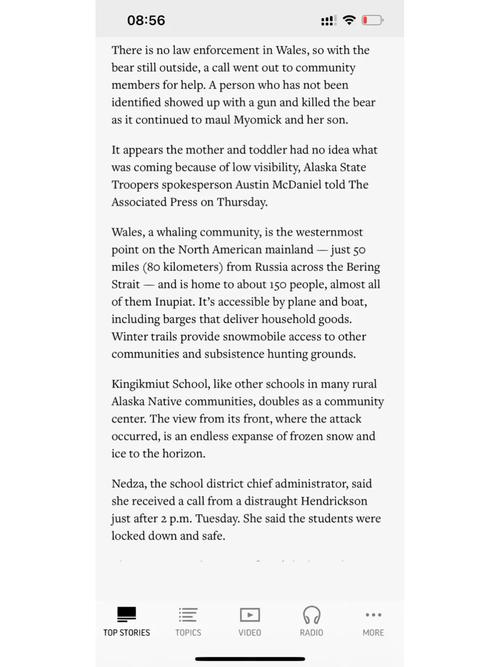
- Solar Radiation Sensors: These sensors are designed to measure the intensity of solar radiation at different angles.
- Satellite Data: Satellites equipped with sensors can provide data on the angle ‘a’ and its impact on polar regions.
- Ground-Based Observations: Researchers conduct ground-based observations to measure the angle ‘a’ and its effects on local environments.
By utilizing these measurement techniques, scientists can gather valuable data on the angle ‘a’ and its influence on polar regions, contributing to a better understanding of Earth’s climate system.
Conclusion
Understanding the angle ‘a’ at which solar radiation strikes the Earth, particularly in polar regions, is vital for comprehending various environmental and climatic phenomena. By analyzing the impact of this angle on polar regions, we can better predict and mitigate the effects of climate change in these sensitive areas. As we continue to study the angle ‘a’ and its influence on Earth’s climate system, we can work towards a more sustainable future.
