1 Million Solar Mass Black Hole: A Multidimensional Exploration
Have you ever wondered about the fascinating world of black holes? Imagine a black hole with a mass equivalent to a million suns. This colossal entity, known as a 1 million solar mass black hole, is a marvel of the cosmos. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of this celestial wonder, exploring its properties, formation, and impact on the universe. Get ready to embark on a journey through the realms of astrophysics and the mysteries of the cosmos.
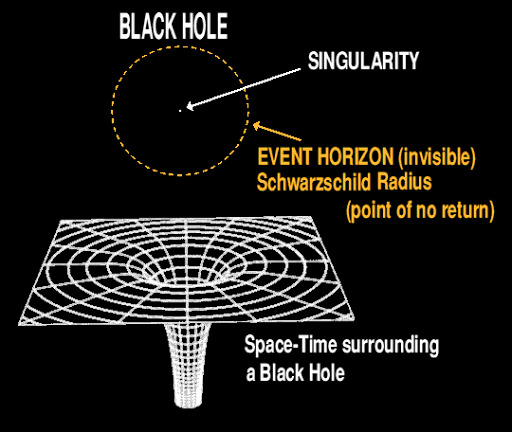
Understanding the Schwarzschild Radius
The Schwarzschild radius is a crucial parameter that defines the size of a black hole. It is the radius at which the escape velocity equals the speed of light. For a 1 million solar mass black hole, the Schwarzschild radius can be calculated using the formula: ( r_s = frac{2GM}{c^2} ), where ( G ) is the gravitational constant, ( M ) is the mass of the black hole, and ( c ) is the speed of light. Let’s plug in the numbers and find out the exact value.
| Gravitational Constant (G) | 6.67430 脳 10^-11 m^3 kg^-1 s^-2 |
|---|---|
| Speed of Light (c) | 3 脳 10^8 m/s |
| Mass of the Black Hole (M) | 1 million solar masses |
By substituting the values into the formula, we find that the Schwarzschild radius of a 1 million solar mass black hole is approximately 1.9 脳 10^6 meters. This means that anything within this radius, including light, cannot escape the gravitational pull of the black hole.
Formation of a 1 Million Solar Mass Black Hole
Black holes are formed through various processes in the universe. One of the most common ways is the gravitational collapse of massive stars. When a star with a mass several times greater than the Sun exhausts its nuclear fuel, it undergoes a supernova explosion. The core of the star collapses under its own gravity, forming a black hole.
In the case of a 1 million solar mass black hole, the formation process is slightly different. These black holes are believed to be formed through the merging of smaller black holes or the collapse of supermassive stars. The merging of black holes is a result of the gravitational interactions between them, leading to the formation of a more massive black hole.
Supermassive stars, on the other hand, are formed through the collapse of massive molecular clouds. These clouds contain a vast amount of gas and dust, which collapse under their own gravity, forming a protostar. As the protostar continues to accumulate mass, it eventually reaches a critical point where it can no longer sustain nuclear fusion, leading to a collapse and the formation of a black hole.
Properties of a 1 Million Solar Mass Black Hole
Now that we understand the formation of a 1 million solar mass black hole, let’s explore its properties. These black holes possess several fascinating characteristics that make them unique in the universe.
1. Strong Gravitational Pull: As mentioned earlier, the Schwarzschild radius of a 1 million solar mass black hole is approximately 1.9 脳 10^6 meters. This means that anything within this radius, including light, cannot escape the gravitational pull of the black hole. The immense gravitational force is what makes black holes so intriguing and mysterious.
2. Event Horizon: The event horizon is the boundary around a black hole beyond which nothing can escape. For a 1 million solar mass black hole, the event horizon is approximately 1.9 脳 10^6 meters. This means that anything that crosses this boundary will be pulled into the black hole, never to be seen again.
3. Accretion Disk: As matter spirals into a black hole, it forms an accretion disk around it. This disk is composed of gas, dust, and other debris that are being pulled in by the black hole’s gravitational force. The intense friction and pressure in the accretion disk can lead to the formation of high-energy jets and X-rays.
