10/14 Solar Eclipse: A Detailed Multi-Dimensional Introduction
Are you curious about the upcoming solar eclipse on October 14th? If so, you’ve come to the right place. This article will delve into the details of this celestial event, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of what to expect and how to witness it. Let’s embark on this journey of discovery.
What is a Solar Eclipse?
A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the Earth and the sun, casting a shadow on our planet. This natural phenomenon can be categorized into three types: total, partial, and annular. On October 14th, we will witness a partial solar eclipse, where the moon covers only a portion of the sun’s disk.
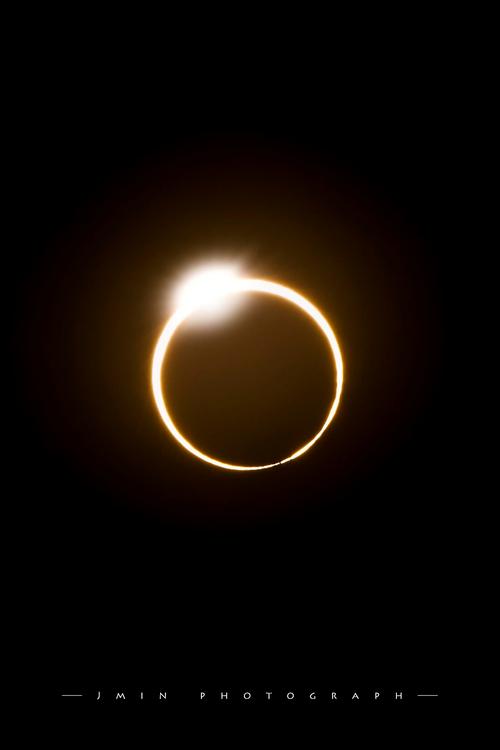

When and Where Can You See It?
The partial solar eclipse will be visible from parts of North America, South America, and parts of the Pacific Ocean. The event will begin at 10:33 AM UTC and reach its maximum coverage at 12:45 PM UTC. To determine if you can see the eclipse in your area, check the local times provided by NASA’s eclipse website.
Here’s a table showing the eclipse times for some major cities:
| City | Eclipse Start | Eclipse Maximum | Eclipse End |
|---|---|---|---|
| New York City | 10:33 AM EDT | 12:45 PM EDT | 2:55 PM EDT |
| Los Angeles | 7:33 AM PDT | 9:45 AM PDT | 11:55 AM PDT |
| London | 3:33 PM BST | 5:45 PM BST | 7:55 PM BST |
How to Safely View the Eclipse
Looking directly at the sun during a solar eclipse can cause permanent eye damage. To safely view the eclipse, you’ll need special solar eclipse glasses or a pinhole camera. These tools will allow you to safely observe the sun’s disk as the moon covers it.
Here are some tips for safely viewing the eclipse:
- Use solar eclipse glasses or a pinhole camera to view the sun’s disk.
- Do not look at the sun without proper protection.
- Do not use sunglasses or regular glasses to view the eclipse.
The Science Behind the Eclipse
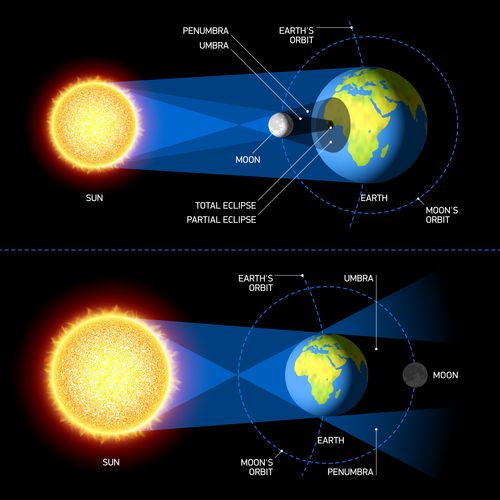
The solar eclipse is a fascinating event that has intrigued scientists and astronomers for centuries. It’s a perfect example of the delicate balance between the Earth, moon, and sun. The moon’s orbit around the Earth is tilted at an angle of about 5.1 degrees, which is why solar eclipses don’t occur every month.
During a solar eclipse, the moon’s shadow can be divided into three parts:
- Umbra: The central, darkest part of the shadow, where the sun is completely blocked.
- Penumbra: The outer part of the shadow, where the sun is partially blocked.
- Antumbra: The region between the umbra and penumbra, where the sun is only slightly blocked.
The Cultural Significance of Solar Eclipses
Solar eclipses have been a source of fascination and fear throughout history. In many cultures, they were believed to be omens or signs of impending doom. However, modern science has helped us understand these events and appreciate their beauty.
Today, solar eclipses are celebrated as a rare and awe-inspiring natural phenomenon. They bring people together, fostering a sense of wonder and curiosity about the universe.
Conclusion
The upcoming solar eclipse on October 14th promises to be a spectacular event. By understanding the science behind it and taking the necessary precautions, you can safely witness this celestial spectacle. So mark your calendars, gather your family and friends, and prepare to be amazed by the beauty of the cosmos.
